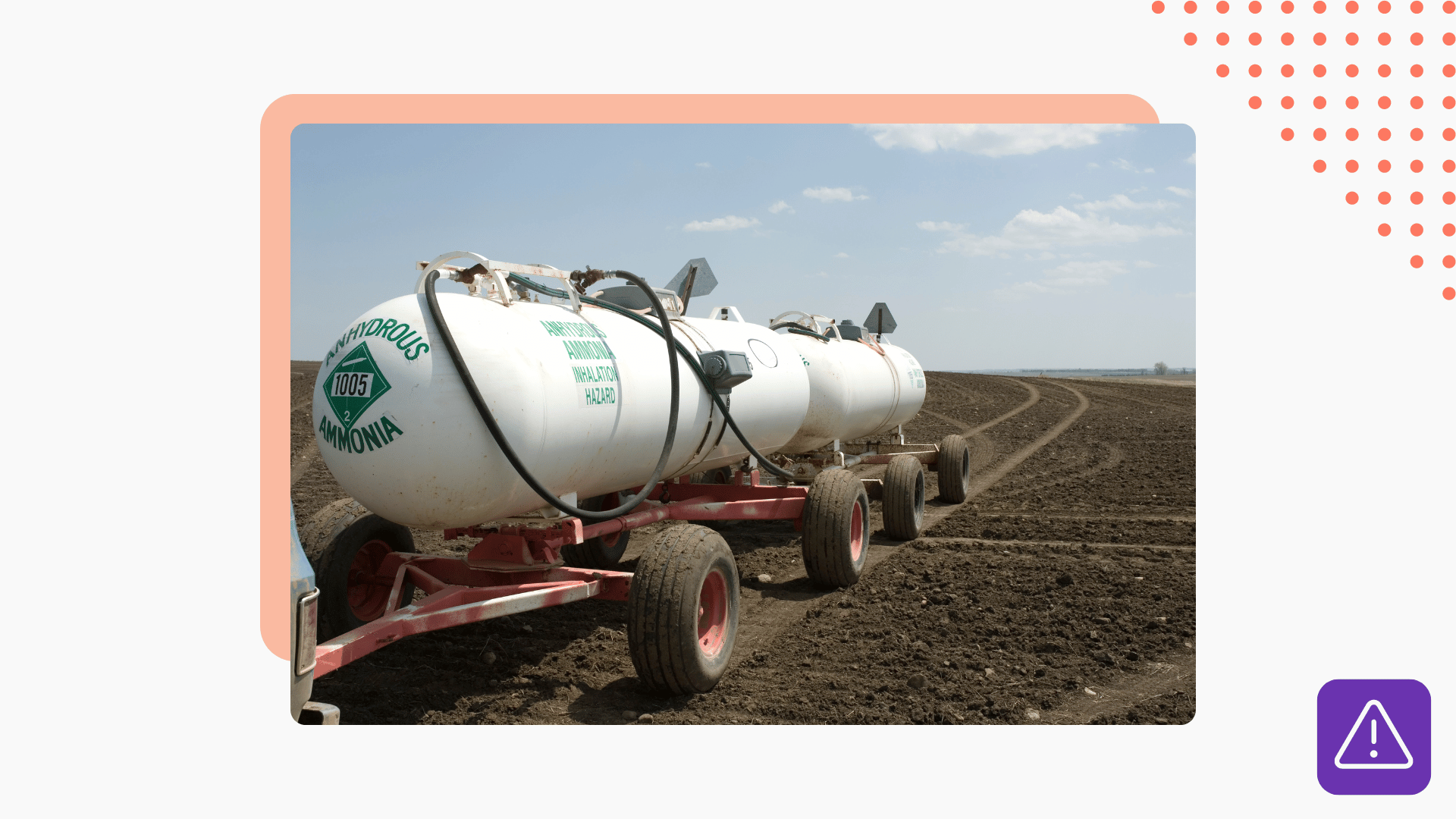
Due to the safety risks that ammonia poses to both workers and the environment, its use in industrial systems falls under OSHA’s PSM requirements. Compliance can be overwhelming given how many components there are to the standard. But once you have a solid ammonia process safety management program in place, compliance is a matter of consistent review and improvement.
PSM vs. RMP
OSHA’s process safety management (PSM) standard and the EPA’s risk management plan (RMP) regulation are very similar. Both regulate the use, storage, handling, and manufacturing of highly hazardous chemicals. While PSM focuses on employee health and safety, RMP focuses on environmental protection.
Process safety management applies to industrial systems that contain 10,000 pounds or more of ammonia. And in March 2023, the EPA expanded its RMP rule “to improve chemical process safety, to assist in planning, preparing for, and responding to accidents, and to increase public awareness of chemical hazards at regulated sources.”
Overview of PSM requirements
Process safety management prevents the accidental release of hazardous chemicals in the workplace. Industrial ammonia refrigeration systems fall under PSM because they function at elevated pressure levels and pose significant exposure risks.
There are 14 elements to PSM compliance which include:
- Employee participation
- Process safety information
- Process hazard analysis
- Operating procedures
- Employee training
- Contractor training
- Pre-startup safety review (PSSR)
- Mechanical integrity
- Hot work permit
- Management of change (MOC)
- Incident investigation
- Compliance audits
- Trade secrets
While the standard includes requirements for what to include in a PSM program, it doesn’t dictate what compliance looks like. For example, under the mechanical integrity component, companies must “establish and implement written procedures to maintain the on-going integrity of process equipment.”
There’s no specific requirement for what those procedure documents should look like, so many companies struggle with creating their programs from scratch.
Ammonia process safety management resources
The best place to start is determining whether ammonia process safety management rules apply to any of the systems within your company. Like most areas of regulatory compliance, breaking the requirements down into separate parts is the easiest way to go.
Here are some additional PSM resources you can visit to learn more about compliance:
- Frontline PSM resource page
- PSM standard 1910.11
- Overview of the RMP rule
- OSHA ammonia refrigeration page
At Frontline, we specialize in helping companies achieve PSM compliance with our effective management tool, Frontline MOC. We built this system with OSHA’s requirements in mind. But it’s also great for tracking non-PSM changes to policies, personnel, procedures, and equipment. If you’ve already got a PSM program in place, Frontline MOC is a great tool to take it to the next level.
Other posts you might like…
No posts