Within the first half of 2022, there were more than 20 trench accident-related deaths in the U.S. While OSHA regulations for trench work have been around for a long time, this rise in deaths caused the agency to pursue a stricter enforcement strategy. And companies that conduct excavation projects must maintain rigorous standards for the protection of trench workers by implementing a variety of measures.
Specific excavation requirements
CFR 29 1926.651 is an OSHA regulation for trench work and other excavation projects. Here are some of the key points that pertain to trenches specifically.
Trench access and egress
Under paragraph (c), you’ll find some information about trench access and egress points. This section ensures that companies provide things like steps, ramps, and ladders so workers can safely get in and out of trenches.
Accumulation of water
Paragraph (h) states that employees should not work in trenches if water is accumulating, unless the company has taken extra steps to protect them from the water. Some examples of safety measures here include using lifelines to keep workers afloat or implementing water removal systems.
Trench inspections
OSHA regulations for trench work also mandate daily inspections of the trench and surrounding work area. The purpose of these inspections is to assess safety risks and identify hazards that need to be addressed. Paragraph (k) dictates that employers must also perform inspections after heavy rainfalls or when the hazards present in the trench change.
Placement of excavated materials and equipment
Under paragraph (j) of this standard, OSHA states that any excavated materials like rocks and soil must be placed at least two feet away from the edge of the trench. The same goes for heavy machinery and equipment. And that’s to prevent heavy buildups of material or equipment from causing a cave-in.
Hazardous atmospheres
Companies must also regularly test the atmosphere in and around trenches to make sure it’s safe for workers. The atmosphere must contain at least 19.5% oxygen per OSHA’s guidelines. Under the information in paragraph (g), safety precautions for hazardous atmospheres include providing respirators and ventilation systems.
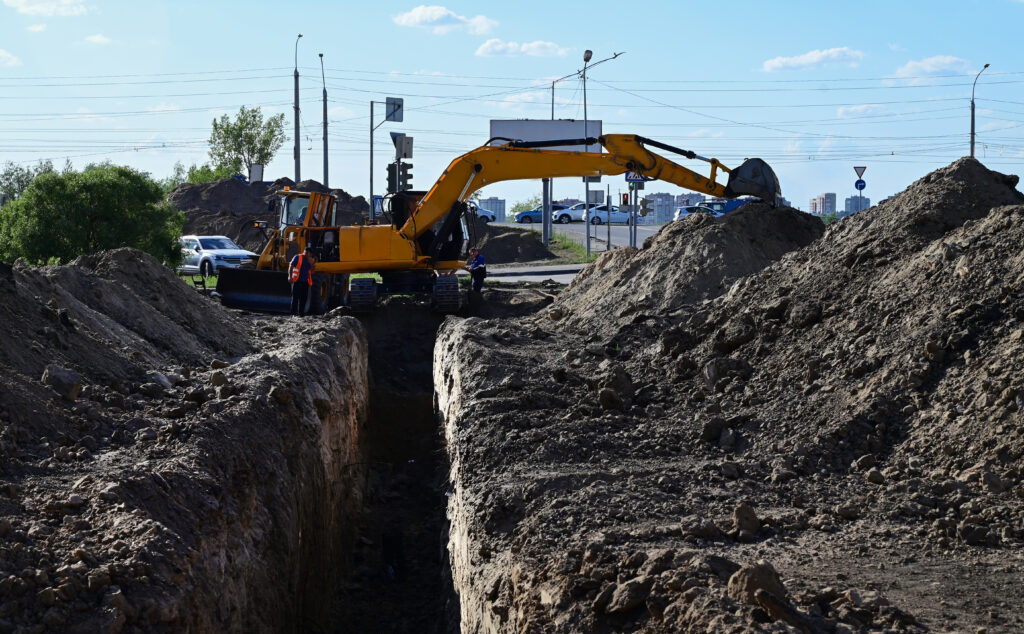

Protective system requirements
OSHA regulation 29 CFR 1926.652 covers workplace protections for excavation projects. This standard ensures employers have adequate protective systems for potential cave-ins.
It requires companies to implement protective measures to prevent cave-ins and reduce injuries if cave-ins occur. Some examples of measures you can implement in compliance with this standard are:
- Shoring the trench walls
- Creating slopes and benches in the walls
- Adding trench shields (boxes)
Sections (e)(2) and (g)(2) of this regulation includes some extra precautions for trench excavations. They provide guidelines for how far the excavation can go past the bottom of the support systems in place.
Protective equipment
The materials and equipment section (d) requires employers to have sufficient personal protective equipment to guard against falling or rolling materials. Hard hats are a good example of PPE to mandate for your team.
Compliance with OSHA regulations for trench work
Given the risks of trench and excavation work, it’s important to consistently audit your compliance. Performing a risk assessment of these work areas can help you identify new hazards and risks that need controlling.
Using EHS software, like Frontline ACT, to coordinate and track corrective actions is a great way to stay on top of compliance tasks. Because everything’s documented in the cloud, you can more easily overview excavation projects and create solutions for hazard control.